The second trimester starts from the end of the 13th week of pregnancy to the last day of the 27th week of pregnancy.
It is sometimes referred to as the “honeymoon phase” since it is a time when you feel relatively good with minimal uncomfortable symptoms.
You’ll feel less queasy and less likely to vomit. You will need to use the restroom less frequently, breasts will be less sore, and you will feel less tired.
.At around 18 to 20 weeks of pregnancy, you will begin to feel the first fetal movements. A fetal doppler also makes the fetal heart sound audible.
Fetal growth can vary significantly for a number of reasons, but at the beginning of the second trimester, your baby will be around 10 cm (4 in) and weigh in at around 28 g (1 oz). By the time your second trimester ends, the baby will be about 35 cm (14 in) long and weigh from 1 to 2 kg (2 to 4 lbs)
What are the symptoms of the Second Trimester of pregnancy?
Enlargement of the abdomen
Gradual enlargement of the abdomen is the most visible symptom of the second trimester.
The uterus grows larger until it is visible above the pelvic bones. If you lie on your back, flex your knees, and gently palpate your lower abdomen, you will feel the uterus – it is a firm, non-tender mass immediately above your pelvic bones.
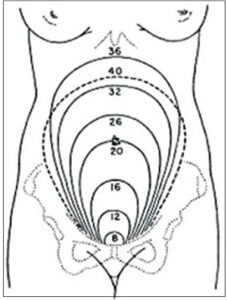
The figure below indicates the height of the uterus at different weeks. You are twelve weeks along when the height of the uterus is barely perceptible. You are 24 weeks pregnant when the upper edge of your uterus meets the upper edge of your umbilicus. The umbilicus’ lower margin is 22 weeks old.
The uterus descends below the level of 36 weeks at term, or 40 weeks, but it enlarges on the sides, making the flanks of the abdomen rather full.
In very tall women, the uterus may appear to be shorter than the GA, whereas in very short women, the uterus may appear to be taller than the GA.
Breast Enlargement
The breast soreness will be less than in the first trimester but the breasts will continue to enlarge in size throughout the second trimester.
The areolas get darker and more pigmented, and the nipple becomes more prominent.
The skin around the areola may also become pigmented and darker – this is known as the “secondary areola”.
You may notice several little lumps along the edge of your areola. These are known as “Montgomery’s tubercles,” . The secretions of these tubercles help keep the nipples and areola flexible and well-moisturized so that they can work well during breastfeeding. They may grow larger and more noticeable in the later part of the second trimester and the early part of the third trimester.
You may also notice little bluish veins on the breast as the breasts enlarges.
Stretch marks or stria may also form on the edges of the breasts in overweight women, especially on the lower and outer parts of the breasts. Stretch marks may also be seen on the shoulders and arms.
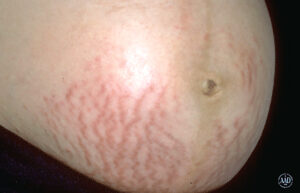
Stria Gravidarum (Stretch Marks)
Stretch marks, or stria gravidarum, usually first appear in the later half of the second trimester or the beginning of the third trimester.
Stretch marks occur when the middle layer of skin, called the dermis, tears and breaks due to rapid stretching of the skin under the pressure of the growing uterus.
The stretching of the skin causes collagen and elastin, which support the skin, to rupture. The blood vessels may show through the tears and the striae first appears as thin, reddish or purple lines. But as they age and heal, they take on a light, silvery hue. As a consequence, later in pregnancy, it’s possible to identify both newly formed purple striae and silvery striae that have healed.
Women who frequently exercise and have strong abdominal muscles have minimal or no striae because the weight of the uterus is supported by the muscles rather than by the skin.
Fetal Movements
The initial movements of the fetus felt by the mother is also known as “Quickening”. If this is your first pregnancy, you will begin to feel the first movements of the baby between weeks 18 and 20. Women who are more experienced and are expecting their second or third baby may feel it earlier, between weeks 16 and 18.
The majority of women report the first fetal movements as a fleeting, faint fluttering sensation deep inside their belly that appears and disappears in an instant. Many describe it as ‘like the fluttering of a butterfly’. Others describe it as a sharp throbbing sensation that arises for a brief period of time before going away.
You might not even be aware of when it originally started because the movements can be very subtle and develop very gradually.
Fetal Heart Sound
At around the 16th week, a stethoscope or fetal Doppler may pick up the fetal heart sound (FHS).The baby’s position and the mother’s weight both influence how early the sound may be heard. The “faint and distant ticking of a watch placed beneath a pillow” is a common way to describe it.
At 20 weeks, the FHS fluctuates between 140 and 160 beats per minute, and at term pregnancy, it drops to 120 to 140 beats per minute. At term, if the rate is below 100 or above 160, it indicates that the fetus is in danger and a caesarian section is required as soon as feasible.
Linea Nigra
This is a thin, dark line extending from the umbilicus to just above the pelvic bones in the middle. It is also known as the “pregnancy line”. In ladies with dark skin, it is darker.
The linea nigra is caused by increased hormones during pregnancy that stimulate increased pigment production. It can be one of the earliest indicators of pregnancy and may develop in the later part of first trimester. The linea nigra may appear darker as the pregnancy progresses. It serves no purpose and has no specific importance.
Tests in the Second Trimester :
Some important tests need to be done in the second trimester:
Fetal Anomaly Scan :
This is a special, detailed ultrasound done to detect any growth problems in the baby. It is usually done between 18 to 22 weeks together with the Quad test. By this time, all the organs are fully developed and any discrepancy in the growth rate or any anatomical abnormality can be identified.
Quad test:
A quad screen, or quadruple marker test, is a blood test that can be performed between 15 and 22 weeks of pregnancy to determine if a fetus is at risk for birth defects. It is a blood test and helps indicate the risk of genetic disorders such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18), neural tube defects (NTDs), spina bifida, and abdominal wall defects.The test looks for abnormal levels of four pregnancy hormones in the mother’s blood:
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): A protein produced by the baby
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG): A hormone produced in the placenta
- Unconjugated estriol (uE3): A form of estrogen produced in the fetus and placenta
- Inhibin A: A hormone released by the placenta and ovaries
Milestones of Second Trimester:
Nervous system : The fetus’s brainstem, which controls breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure, is almost fully developed by the end of the second trimester at 28 weeks. The brainwave activity begins to include sleep cycles, including REM sleep, when dreaming occurs. Part of the brain that controls motor movements is fully formed. It can respond to stimulus.
Eyes: The fetus’s eyes gradually move to the front of its face.
At 18 weeks, the eyes are developed enough to detect light. Eyebrows begin to form at 22 weeks. At 25–26 weeks, the fetus starts makes melanin, which gives the eyes their color. Eyelashes start to form at this time. At 27 weeks, the baby can open its eyes and blink .
Skeleton: The baby’s bones begin to harden and become larger, especially the long bones and skull. This process is called ossification and involves adding calcium and phosphate to cartilage or membrane tissue to harden it.
Limbs: The limbs develop and become longer. Limb movements become more coordinated. Kicks become stronger. The hand and toe prints are visible, and toe nails form by the end of the second trimester.
Skin: Skin starts to thicken and becomes less tranparent. Lanugo hair, a fine, downy hair that covers a fetus’s body, typically develops between 16 and 20 weeks of gestation, starting from the scalp.
Ears: Ears move to the normal position at the side of the head and by 20 weeks, the baby begins to hear sounds. It can listen to the mother’s heartbeat and by the end of the trimester may turn its head towards the sound of your voice..
Digestive system: The digestive system starts working by the 18th week and by the 21st week, the baby starts to swallow amniotic fluid to to help develop their digestive system further. Meconium starts to form in the intestines. Tooth buds begin to develop beneath the gums.
Lungs: Lungs begin to form tissue that will allow them to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide after birth In the second trimester, the lung tissue is a solid structure without air.
Gender: Gender can be clearly identified by ultrasound.
What are the serious symptoms I should look out for?
Please contact your doctor immediately, if you have
- Severe cramping or abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Headache, especially if you have a high blood pressure. It could be due to a condition known as Pre-eclamptic toxaemia (PET). Other symptoms of PET could include sudden swelling of the legs and blurry vision.
- A fever over 38° C (100° F)
Read More Questions and Answers on Pregnancy and Gynecology

5 Supplements for Women in Menopause
Women in menopause need to take supplements due to declining estrogen, with key focus on Calcium and Vitamin D for osteoporosis prevention.

The Menstrual Period
Your menstrual cycle is an important part of your reproductive health. While most women have a predictable monthly rhythm, it’s also extremely common to have
Obstetric and Gynecological Surgeries
Gynecology has advanced tremendously over the years, offering women safer, gentler, and more precise surgical options. Whether performed for childbirth, pain relief, or reproductive health,

Menopause – Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Menopause is a natural phase in every woman’s life, marking the end of the reproductive years. The ovaries stop producing eggs (ovum) at this time

Menstrual Period Problems
Menstrual periods can be complicated by problems like pain, irregular periods, heavy bleeding or very litlle blood flow. Midcycle bleeding is another common issue.

Infertility – Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Infertility can be due to both male and female factors. Both partners need to be tested and the cause diagnosed for accurate treatment




