Infertility is a condition which can cause considerable stress in both the partners. The causes of infertility and the diagnosis and treatment are different in males and females.
What is Infertility?
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse. For women over 35, this period is reduced to six months. Subfertility, is a condition where conception takes longer than usual, but is still possible without medical intervention.
What are the different types of infertility?
There are two types of infertility:
Primary Infertility : Fertility is said to be primary when a couple has not been able to conceive at all in one year.
Secondary Infertility: Secondary fertility is when someone has previously conceived but is no longer able to. The earlier pregnancy may be a mature full term baby or a miscarriage.
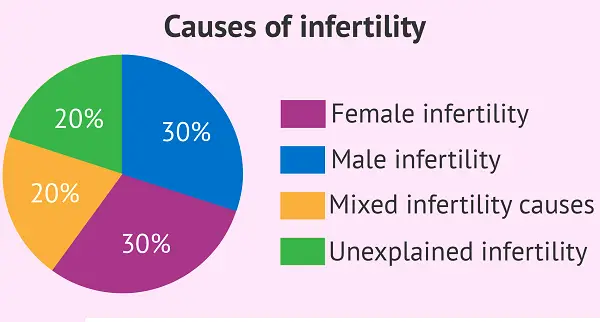
What causes Infertility?
Infertility can be due to problems in either the male partner or the female partner or both.
Causes of Female Infertility:
- Lack of ovulation – All women produce an egg (ovum) once a month – the process is called ovulation and it occurs approximately 14 days from the first day of the last period. Fertilzation of the ovum by a male sperm after sexual intercourse causes a pregnancy. Lack of ovulation is a common cause of female infertility. Conditions like PCOS, Hypothyroidism and Hyperprolactinema are the most common causes of lack of ovulation.
- Blocked fallopian tubes – Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes can prevent sperm from reaching the egg or block the fertilized egg from reaching the uterus. This can be caused by pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, or previous surgeries.
- Problems in the genital tract – Abnormalities with the uterus or cervix, such as polyps, fibroids, or issues with the cervical mucus, can interfere with implantation or increase the risk of miscarriage.
- Endometriosis: This condition occurs when the tissue that normally lines the inside of your uterus ( endometrium) grows outside of it. It can affect the function of the ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes.
- Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI): Also known as premature ovarian failure, this condition occurs when the ovaries stop functioning normally before age 40.
Causes of Male Infertility:
- Sperm Production Issues: Low sperm count, poor sperm motility (movement), or abnormal sperm shape can hinder conception. These issues can stem from genetic conditions, infections, or lifestyle factors.
- Varicocele: This is a swelling of the veins that drain the testicle, which can result in reduced sperm quality.
- Ejaculation Disorders: Conditions like retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting through the penis, can prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Issues with hormones produced by the testicles, pituitary gland, or hypothalamus can affect sperm production.
- Structural Problems: Blockages in the tubes that carry sperm can prevent them from getting into the ejaculate.
How is Infertility Diagnosed?
Diagnosing infertility involves a series of tests and evaluations to identify the underlying cause. It is different in men and women.
Tests for Women
- Ovulation Testing: It is important to identify if the female partner is ovulating every month. This can be done by testing for hormones like estrogen, progesterone, S. TSH and FSH. Ultrasounds at the time of ovulation can also help diagnose ovulation .
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG): This X-ray procedure checks for blockages in your fallopian tubes and assesses the shape of your uterus.
- Ovarian Reserve Testing: This involves blood tests to determine the quantity and quality of your eggs. Tests for the hormone AMH ( Anti-Mullerian Hormone) can help identify fertility and the possibility of regular ovulation.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound can visualize the ovaries and uterus to identify potential issues like fibroids or cysts.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgery to examine the pelvic organs for conditions like endometriosis or scarring may be necessary.
Tests For Men
- Semen Analysis: Semen Analysis is the most important test to check for fertility in men. This test evaluates the health and viability of sperm, including their count, movement, and shape.
- Hormone Testing: Blood tests check levels of testosterone and other hormones essential for sperm production.
- Scrotal Ultrasound: This can help detect varicoceles or other structural abnormalities.
- Genetic Testing: Identifies genetic causes of infertility, especially in cases of very low sperm counts.
Treatment for Infertility
Treatment depends on the cause of infertility, but there are several options available that can significantly increase your chances of conception.
For Women
- Medications: Drugs like Clomiphene citrate (Clomid) or letrozole (Femara) stimulate ovulation. Gonadotropins are injectable hormones that can also promote egg production.
- Surgery: Procedures to remove polyps, fibroids, or repair blocked fallopian tubes can improve fertility.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Sperm is placed directly into the uterus during ovulation.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Eggs are retrieved from the ovaries, fertilized with sperm in a lab, and the resulting embryos are transferred to the uterus.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol can improve fertility.
For Men
- Medications: Hormone treatments or medications that address infections or inflammation can improve sperm production.
- Surgery: Varicocele repair or surgeries to clear blockages in the sperm delivery system.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
- IUI: Directly placing sperm into the uterus.
- IVF/ICSI: Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) involves injecting a single sperm directly into an egg during IVF.
- Lifestyle Changes: Improving diet, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and avoiding heat exposure to the testicles can enhance sperm quality.
Preventing Infertility and Improving Fertility
While not all causes of infertility can be prevented, there are steps you can take to improve your reproductive health.
General Tips for Both Men and Women
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being either underweight or overweight can affect hormone levels and ovulation in women, and sperm production in men.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall health and fertility.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular, moderate exercise can improve your fertility, but avoid excessive physical activity which might have the opposite effect.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Both can impair fertility in men and women.
- Limit Caffeine: High caffeine intake has been linked to reduced fertility.
- Reduce Stress: High stress levels can interfere with ovulation and sperm production. Techniques like yoga, meditation, and counseling can be beneficial.
Specific Tips for Women
- Monitor Your Cycle: Keeping track of your menstrual cycle can help you understand your fertile window.
- Avoid Excessive Use of Lubricants: Some lubricants can negatively affect sperm movement. Look for fertility-friendly options.
- Prenatal Vitamins: Taking prenatal vitamins, particularly folic acid, can prepare your body for a healthy pregnancy.
Specific Tips for Men
- Keep Cool: Avoid hot tubs, saunas, and tight underwear which can raise the temperature of the testes and affect sperm production.
- Avoid Toxins: Exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, and other toxins can reduce sperm quality. Use protective gear if you work in environments with these hazards.
Conclusion
Infertility is a multifaceted issue with numerous potential causes, but with the right diagnosis and treatment, many couples are able to conceive.
Read Questions and Answers on Pregnancy and Gynecology
HPV: 10 Important Facts
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can cause warts and cancers. There are more than 100 strains of HPV, some more dangerous than the others.
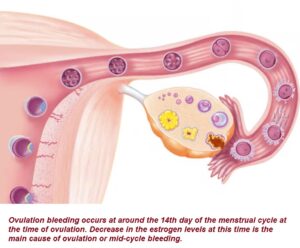
Ovulation Bleeding: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Ovulation bleeding, also known as mid-cycle bleeding occurs at around the 14th day of the menstrual cycle.
Is Abdominal Pain Normal in Early Pregnancy? Understanding Cramps and Common Causes at 8 Weeks
Dr. Madhumita Mazumdar recently had a consultation with a young woman experiencing abdominal pain during early pregnancy. This blog post aims to address the concerns
Understanding Abdominal Pain During Early Pregnancy: Causes, Cramps, and What’s Normal at 8 Weeks
Abdominal Pain During Early Pregnancy: Understanding the Causes and Solutions Pregnancy is an exciting time, but it can also bring unexpected challenges. Recently, I had
Uterine Fibroids: Understanding Heavy Bleeding, Severe Pain, and When Surgery May Be Needed
Uterine Fibroids: A Patient’s Journey to Diagnosis and Treatment Uterine fibroids, learn more about uterine fibroids, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the
Ovarian Cyst vs Ovarian Tumor: Answering Your Questions About Solid Cysts, Tumor Risks, and Differentiating Ovarian Cancer
Patient: Dr. Mazumdar, I’ve been experiencing pain in the lower part of my abdomen. What could be causing this? Dr. Mazumdar: I understand you’re concerned


