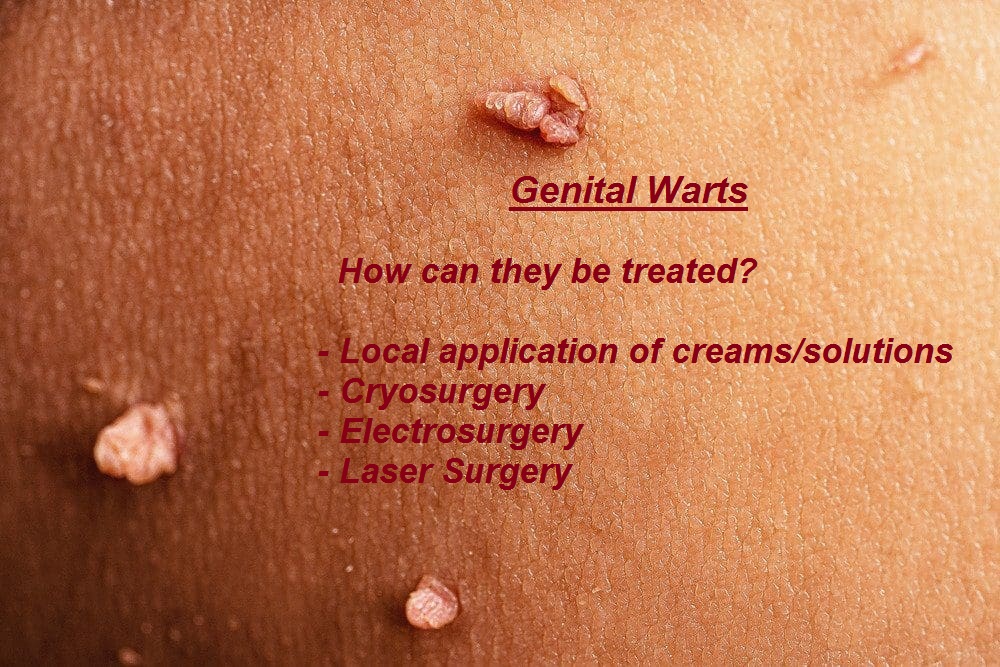
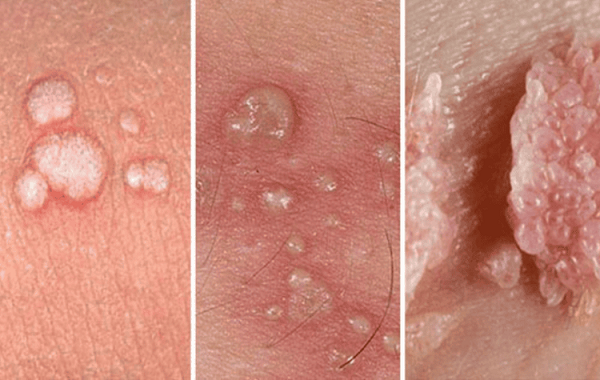
When you hear the term “genital warts,” it can be a little intimidating, but it’s important to know that you’re not alone and that they are quite common. Genital warts are one of the most prevalent sexually transmitted infections (STIs), caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Let’s walk through everything you need to know about genital warts, from their causes and symptoms to the different treatment options available. I’ll break things down step-by-step so that you feel informed and confident about how to approach this condition.
What Causes Genital Warts?
Genital warts are caused by certain strains of HPV, specifically types 6 and 11, which are considered low-risk HPV types. Unlike the high-risk types (such as HPV 16 and 18, which are linked to cervical cancer), the strains responsible for genital warts typically do not lead to cancer.
HPV is primarily transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It’s worth noting that HPV can be passed even if there are no visible warts or other symptoms, which is why it spreads easily. Your immune system plays a major role in how your body handles the virus. Some people may come into contact with HPV and never show any symptoms, while others may develop warts.
Symptoms of Genital Warts
Genital warts can vary in appearance and may not always be easily noticeable. They usually appear as small, flesh-colored bumps or clusters of bumps in the genital or anal area. The warts can be flat or slightly raised, and sometimes they have a cauliflower-like texture.
In women, genital warts can appear on the vulva, inside the vagina, on the cervix, or around the anus. In men, they can occur on the penis, scrotum, or around the anus. Warts can also develop in the mouth or throat, though this is less common and usually results from oral sex with someone who has the virus.
Some people may not notice any discomfort, while others might experience symptoms like itching, tenderness, or mild pain. Because warts can be small or hidden within the folds of skin, they can be easy to miss at first.
Different Treatment Options for Genital Warts
When it comes to treating genital warts, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The good news is that genital warts are treatable, and there are several methods available depending on factors like the size, location, and number of warts, as well as your personal preferences. Let’s go through some of the main treatments, how they work, and the pros and cons of each.
- Topical Medications
Topical treatments are creams or solutions that you can apply directly to the warts. These are generally the first line of treatment, especially if the warts are small and external. There are several types of topical medications available:
- Imiquimod (Aldara, Zyclara): This cream helps boost your immune system so it can fight off the HPV virus more effectively. You’ll apply it at home, usually a few times a week.
- Advantages: One of the benefits of imiquimod is that it helps your body clear the virus, not just the wart itself. It’s an easy-to-use, non-invasive option.
- Disadvantages: It may cause redness, irritation, or peeling in the area where you apply it, and it can take several weeks to work.
- Podofilox (Condylox): Another topical solution, podofilox works by destroying the wart tissue directly. You can also apply this medication at home, usually twice a day for a few days, followed by a break.
- Advantages: It’s relatively easy to use, and since you can apply it at home, it’s convenient.
- Disadvantages: Like imiquimod, it can cause skin irritation and discomfort at the application site. It also doesn’t address the underlying virus, so there’s a chance that the warts may return.
- Sinecatechins (Veregen): This is a green tea extract that is applied to warts several times a day. It’s a newer option and works similarly to other topicals by promoting the healing of warts.
- Advantages: It’s plant-based, which may appeal to people looking for a natural option.
- Disadvantages: It can cause skin irritation and might take time to see results.
- Cryotherapy (Freezing)
Cryotherapy is a procedure where liquid nitrogen is used to freeze and destroy the wart tissue. This is usually done in a doctor’s office and may require multiple treatments depending on the size and number of warts.
- Advantages: Cryotherapy is a quick, in-office treatment that is often very effective. It works by causing the wart tissue to die off and fall away over time.
- Disadvantages: It can be uncomfortable, and you may experience blistering, swelling, or pain after treatment. Multiple sessions may be needed, and there’s a chance of scarring.
- Electrosurgery (Burning)
Electrosurgery involves using an electric current to burn off the warts. This procedure is typically done under local anesthesia to reduce pain.
- Advantages: Electrosurgery can be very effective for larger or stubborn warts. It’s usually a one-time treatment, and the results are immediate.
- Disadvantages: This method can be painful, and recovery might involve soreness or scabbing. There’s also a risk of scarring.
- Laser Treatment
Laser therapy uses a high-intensity beam of light to destroy the wart tissue. It’s often used for warts that are difficult to treat with other methods or when they’re located in sensitive areas.
- Advantages: Laser treatment can be a good option for hard-to-reach warts or for warts that haven’t responded to other treatments. It’s precise and can be done quickly.
- Disadvantages: Laser treatment is usually more expensive and may require anesthesia. You may experience some discomfort during and after the procedure, and scarring is a potential risk.
- Surgical Excision
In some cases, your doctor might recommend surgically removing the warts. This is typically done with a scalpel or a small tool under local anesthesia.
- Advantages: Surgical removal is very effective, especially for large or extensive warts. It’s also immediate, so you don’t have to wait for the warts to go away over time.
- Disadvantages: Surgery can be uncomfortable, and recovery time varies. There’s also a risk of scarring, and, like with other treatments, warts can still come back if the virus isn’t fully cleared from your system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Treatment
As you can see, each treatment option has its pros and cons. Here’s a quick comparison to help you weigh the options:
- Topical medications are convenient but might take weeks to work and can cause irritation. They’re good for small, external warts and can be used at home.
- Cryotherapy is quick but might require multiple sessions. It’s great for smaller warts but can cause temporary discomfort.
- Electrosurgery and laser treatments are effective for more stubborn warts, but they can be painful and come with higher costs.
- Surgical removal is usually a one-time fix, but it comes with the risk of scarring and discomfort.
The best treatment for you will depend on the size, number, and location of your warts, as well as your personal preferences and how you feel about potential side effects or downtime.
Potential Complications
It’s important to note that while treatments can remove warts, they don’t cure HPV. The virus can remain in your body, meaning that warts could potentially return in the future. Additionally, HPV can still be transmitted to others even after warts are treated. That’s why using condoms or other protective measures during sex is still important, although condoms don’t offer complete protection since HPV can affect areas not covered by a condom.
Other potential complications include skin irritation, pain, or scarring from treatments. In rare cases, untreated genital warts can grow larger or spread. In some individuals, especially those with weakened immune systems (such as those with HIV), warts can be more difficult to treat and may recur more frequently.
Preventing Genital Warts
Prevention is always better than treatment, and the best way to prevent genital warts is through vaccination. The HPV vaccine, typically given to adolescents, protects against the strains of HPV that cause genital warts as well as those that can lead to cancer. If you haven’t received the vaccine and are eligible, it’s worth considering.
In addition to vaccination, practicing safer sex by using condoms and having open conversations with sexual partners can help reduce your risk of contracting or spreading HPV.
Final Thoughts
Dealing with genital warts can be stressful, but remember, it’s a common and treatable condition. By understanding your treatment options and discussing them with your doctor, you can find the right approach for your situation. Don’t hesitate to ask questions, and know that with time, the right treatment will help you get back to feeling like yourself again.