What are birth control methods (contraception)?
Contraception or birth control methods refers to the methods or devices which are used to prevent pregnancy. They give you control over your own reproduction health and you can decide when or if you want to have children.
Why Use Birth Control Methods?
People use birth control methods for various reasons:
- Preventing Unplanned Pregnancies: Unplanned pregnancies can cause emotional, financial, and physical challenges – a birth control method properly used can help avoid these issues.
- Family Planning: To decide the number and spacing of children.
- Health Reasons: Some individuals use contraception to avoid pregnancy due to health conditions.
- Control Over Reproductive Health: To gain control over one’s reproductive life and timing.
What are the different types of birth control methods?
There are several types of birth control methods, each with its own use, benefits, and drawbacks. They can be categorized into:
- Barrier Methods
- Hormonal Methods
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
- Natural Methods
- Emergency Contraception
- Permanent Methods

Barrier Methods
Barrier methods are methods which prevent the sperm from reaching the egg. They include:
Male Condoms
Male condoms are worn over the penis during intercourse. They are usually made of latex and come in different sizes. They can also be ribbed or dotted and may contain perfume. They are easily accessible at most pharmacies or medical stores. They protect against Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) and since they do not contain hormones, there are no side effects. A disadvantage is that they can break or slip during sexual intercourse. Some people are allergic to latex.
Success rate is about 85 % at preventing pregnancy.
Female Condoms
Female condoms are also made of latex. They are larger than the male condom. And like the male condom, they need to be inserted into the vagina before intercourse and removed later.
The advantages are that they protect against STIs and cause no side effects since they are non-hormonal. But the disadvantage is that they are bulky and can be difficult to insert. They are also more uncomfortable. They are more expensive than male condoms.
Success Rate – around 79% .
Diaphragms and Cervical Caps
Diaphragms are flexible, reusable, saucer shaped devices which are inserted into the vagina just before sexual intercourse. The cervical cap is smaller and thimble shaped. Both need to be inserted just before sexual intercourse and removed later.
Both diaphragms and cervical caps are used together with spermicide gel for more effectiveness – the gel paralyses the sperms.
The advantage is that they do not cause side effects since they do not contain hormones. They are also reusable.
The big disadvantage is that most women find it very difficult to insert the diaphragm as well as the cervical cap and may need a healthcare worker to insert them. And since they need to be used with spermicide gel, there can be irritation from the spermicide gel. There are also increased risks of urinary tract infections.
Success Rate – around 88%.
Hormonal Methods
Hormonal methods act mainly by altering a woman’s hormonal balance to prevent ovulation. They also thicken the cervical mucus, or thin the uterine lining to prevent implantation of the embryo. The common hormonal birth control methods are:
Birth Control Pills
Most Birth control pills contain estrogen and progesterone. Some contain progesterone alone. They come in packets of 21 or 28 pills. One pill needs to be taken daily without missing any. These pills prevent pregnancy by stopping ovulation. They also regulate menstrual cycles and reduces menstrual cramps.
An important disadvantage is that they must be taken daily and some women may occasionally forget to take them, causing hormonal imbalance and withdrawal bleeding. They can also cause side effects like nausea, weight gain and occasional breast pain..
Since they contain hormones, the birth control pills can cause complications like increased risk of blood clots, especially in smokers and older women. The progesterone alone pill does not cause this complication.
The Success Rate at preventing pregnancies is around 91%.
Birth Control Patch
The birth control patch is a small plastic patch which contains estrogen and progestin on one side and is sticky on the other side – it can be stuck to the skin of a part of the body which is not easily visible – for example , to the skin of the under arm or the inner thighs. The patches need to be replaced weekly for 3 weeks. You will get a period on the 4th week.
The advantage is that the patch needs to be applied only once a week and there are less risks of forgetting to take it. And since it does not need to be taken by mouth, there is no nausea or stomach discomfort.
The disadvantage is that, like birth control pills, they also increase the risks of blood clots. There may also be skin irritation at the site of application. They are usually not very effective in women over 198 pounds.
The Success Rate is around 91% .
Birth Control Shot
The birth control shot is an injection containing a hormone called depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA). The common brand name is Depo Provera. The injection is given at a regular schedule of 3 months.
The big advantage is that since it is every 3 months, you do not need to remember to take it every day ( unlike the birth control pills). Also, since it does not pass through the stomach, there are no side effects like nausea and vomiting. Another advantage is that, since it does not contain estrogen, the risks of a blood clot is very low. If taken regularly, the periods may stop or the blood flow in each period may become very less.
The disadvantage is that it may cause weight gain ( like all hormones) and the return to fertility is delayed. There is a also a risk of bone density loss with long-term use
Success Rate: Around 94% .
Vaginal Ring
The vaginal ring is a thin, flexible ring that can be inserted into the vagina. It contains hormones which are slowly released into the vagina. Like all hormonal birth control methods, it works by stopping ovulation and by thickening the cervical mucus.
The ring needs to be inserted into the vagina and kept inside for 3 weeks, When it is removed, you will get your periods. Once the periods are over, you will need to insert a new ring.
Its advantage is that it only needs to be changed once a month. It can also regulate menstrual cycles.
But the disadvantage is that sometimes, it may cause vaginal irritation. It may also slip out during sexual intercourse or when passing urine or stool.
Success Rate: Around 91% .
Hormonal Implants
Also called long-acting reversible contraception, or LARC, a hormonal implant is a small, flexible rod which can be placed under the skin of the upper arm. It releases a low, steady dose of the hormone progestin. Each implant lasts for 3 years and then needs to be replaced by a new one.
The main advantage is that it is a long-lasting, low-maintenance method of birth control. It is also highly effective. While it is present, your periods may stop and you will not get a period for 3 years. This is not harmful and the periods will become normal after it is removed.
Its disadvantages is that it can cause irregular bleeding. Another disadvantage is that it needs a minor procedure for insertion and removal. As with all hormones, it can cause weight gain and mood changes.
Success Rate: Over 99%.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
IUDs are small devices inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
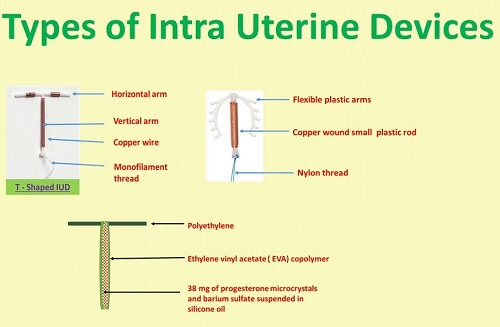
Copper IUD
A copper IUD is a small device which contains copper. It can be T-shaped (it is then called Copper-T) or may be circular in appearance.
It acts in two ways – it changes the way sperm cells move so they can’t swim to an egg and fertilize it. It also prevents implantation of an embryo.
Copper IUDs can last up to 5 or 10 years, depending on the amount of copper it contains.
The copper prevents implantation of the embryo.
Its advantages are that it is long-lasting and hormone-free. It is also highly effective. In initial months, it can cause some amount of cramps and spotting, but over time, these disappear and you will have an uneventful birth control period.
The disadvantage is that it can sometimes can cause heavier periods and cramps. It also needs to be inserted by a healthcare provider. Other risks are that it may occasionally be dislodged from the uterus , it may perforate the uterus during insertion and it may get expelled from the uterus.
Success Rate: Over 99%.
Hormonal IUDs
Intra uterine devices which contain hormones are known as hormonal IUDs. Important brand names are Mirena, Kyleena and Skylar. They work by releasing small amount of hormones inside the uterus. This prevents ovulation and interferes with the endometrial lining to prevent implantation. They act for 3-6 years depending on the brand.
The main advantages are that they are long-lasting and can reduce menstrual bleeding and cramps. So, they can be used in the treatment of heavy menstruation or endometrial hyperplasia.
The disadvantage is that they can cause irregular bleeding initially. They are also expensive and needs to be inserted by a healthcare provider.
Success Rate: Over 99%.
Natural Birth Control Methods
Natural birth control methods are methods in which the menstrual cycle is tracked to identify the fertile days of the cycle. Sexual intercourse is avoided on these fertile days.
Fertility Awareness-Based Methods (FAM) or the Rhythm method
In FAM, the menstrual cycle is tracked with the help of basal body temperature, and changes in the cervical mucus to identify fertile days.
The advantage is that there are no side effects since it does not involve taking any pills or using medical devices.
The main disadvantage is that it needs daily tracking. You will need to be disciplined and very aware of your menstrual cycle. It is not effective in women who have irregular menstrual cycles. It needs to be done accurately. There are higher risks of unintended pregnancy compared to other methods
Success Rate: Around 76%.
Withdrawal Method (Pulling Out)
The withdrawal method is the method in which the penis is pulled out of the vagina just before ejaculation. There are no side effects to this method.
The big disadvantage is that it requires self-control and experience. It is less effective than other methods. It has a higher failure rate. It does not provide any protection against sexually transmitted diseases.
Success Rate: Around 78%
Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception is used after unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy.
Morning-After Pill
The morning after pill contains a high level of progesterone which can prevent ovulation. It can also disrupt the endometrium and prevent implantation of the embryo. It should be taken as soon as possible after unprotected sex, preferably within 24 hours, although it may be effective up to 72 hours.
It is available over-the-counter without a prescription..
But it is not for regular use. It can cause nausea and irregular bleeding if taken frequently. In most women, there may be spotting about 4-5 days after taking the morning after pill.
Success Rate: Around 89% if taken within 72 hours.
Copper IUD (as Emergency Contraception)
Copper IUD can be used as an emergency birth control method. The IUD needs to be inserted into the uterus as early as possible, preferable within 5 days, after sexual intercourse to prevent implantation of the embryo.
The main advantage is that it is very effective. You can continue to use the copper T IUD for ongoing contraception.
The main disadvantage is that it requires insertion by a healthcare provider.
Success Rate: Over 99% if inserted within the appropriate time frame.
Permanent Birth Control Methods
Permanent methods are for individuals who are sure that their family is complete and that they do not want future pregnancies.
Tubal Ligation (Female Sterilization)
Ligation of the Fallopian tubes in females is the commonest method of permanent sterilization. It is a minor surgery in which the tubes are cut and tied, blocking the fallopian tubes.
It is permanent and highly effective.
The main disadvantage is that it is a surgical method. It is not easily reversible.
Success Rate: Over 99%
Vasectomy (Male Sterilization)
Vasectomy or male sterilization is the procedure in which the vas deferens is cut or tied. The vas deferens are the tubes which carry sperm from the testes to the penis.
The main advantage is that it is permanent and highly effective. It is simpler and more easily done than female sterilization.
The disadvantage is that, since it is a surgical procedure, it carries all the risks of surgery. It is not easily reversible.
Success Rate: Over 99% .
Making the Right Choice
Choosing the right contraception depends on various factors including your health, convenience and comfort. Many methods are available which can help you to plan your reproductive life.
Read More Questions and Answers on Pregnancy and Gynecology
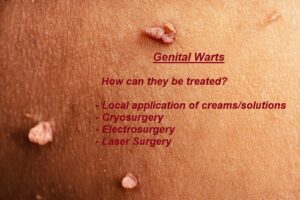
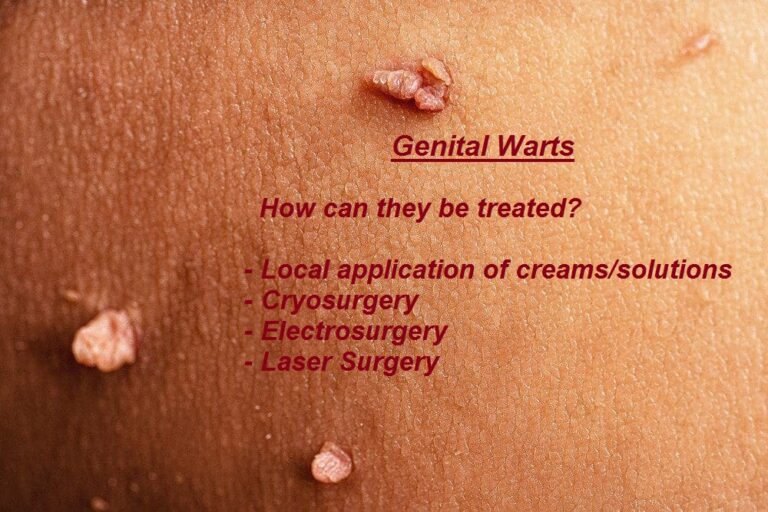
How are Genital Warts treated?
Genital Warts are caused by the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases.

Birth Control methods
Birth Control methods like pills, patches, condoms and IUDs are temporary methods. Permanent methods are tubal ligation and vasectomy. Emergency contraception like pills and Copper Ts are also important.

Vaginitis – Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina causing symptoms like abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain and swelling. It is usually caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.

Sexually Transmitted Diseases -Types, Causes, Spread, Symptoms and Treatment
The common STDs are Syphilis, Gonorrhoea, Chlamydia, Trichomoniasis. Hepatitis B, Herpes simplex virus (HSV), HIV and Human papillomavirus (HPV).

Endometriosis- Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Endometriosis is a condition which causes growth of endometrium outside the uterus, It can cause severe pelvic pain, heavy bleeding and fatigue. It is closely associated with infertility.

The Menstrual Cycle:Phases- Follicular, Luteal, Ovulation and the Period.
The menstrual cycle begins on the first day of one period and ends before the first day of the next. It has 4 phases – the Period, Follicular, Ovulation and the Luteal Phase.