Early pregnancy bleeding , that is, bleeding in the first trimester, can be a deeply distressing experience for many women.
Recently, a young women came in to my clinic in distress. She was around 6 weeks pregnant and had had mild spotting since the last three days. She was afraid that she was heading for a miscarriage.
But bleeding during the first trimester of pregnancy may be due to other simple causes and not always due to a miscarriage.
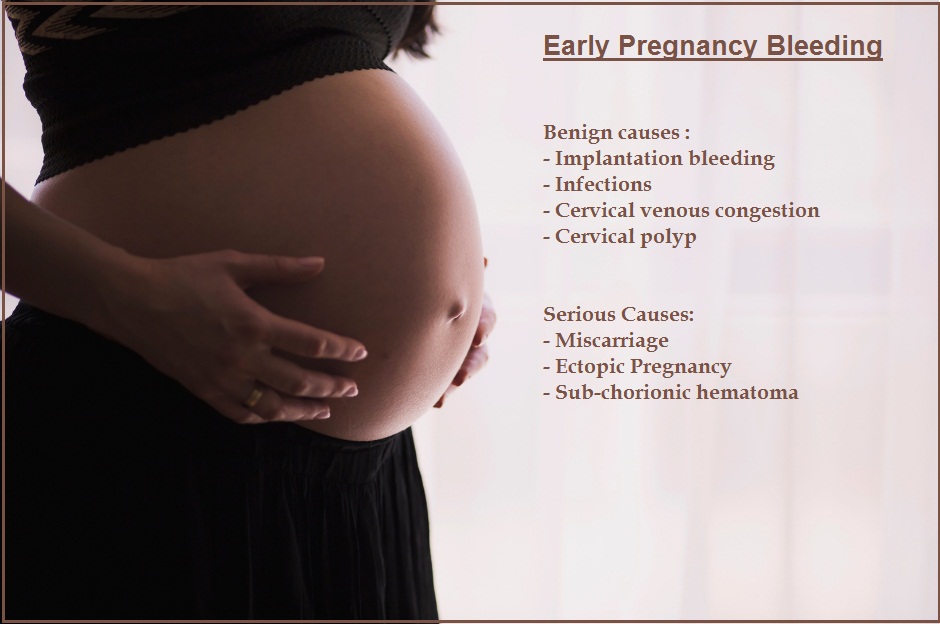
What Causes Early Pregnancy Bleeding?
Spotting or light bleeding during early pregnancy is relatively common and can be caused by several non-threatening factors.
- Implantation bleeding: Occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. It usually occurs at around the time of the missed period, is light and generally clears up in a few days.
- Cervical Venous congestion: Veins in the cervix can get congested, especially in early pregnancy. Pregnancy hormones often lead to an increased blood supply to the cervix, making it more sensitive and prone to spotting.
- Cervical changes: Hormonal shifts can soften and increase blood flow to the cervix, leading to light bleeding.
- Infections or irritations: Conditions such as vaginal infections or recent physical exams may also trigger spotting.
Key Tips:
- Avoid sexual activity if spotting occurs, as this can aggravate cervical sensitivity.
- Consult your doctor if there are cramps or heavy bleeding.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to manage pregnancy-related hormonal fluctuations.
Can Bleeding in Early Pregnancy Be Normal?
Yes, early pregnancy bleeding can be normal. Minimal bleeding or spotting does not always indicate a miscarriage or abnormality. However, an ultrasound must always be done to check on the health of the pregnancy.
Common symptoms of normal bleeding in early pregnancy are:
- Light spotting: Common and typically harmless. The spotting is usually pinkish or brownish. But in some cases, the spotting may be bright red.
- Painless: the spotting is usually painless.
- Post-examination : Bleeding can occur normally after a vaginal examination due to cervical congestion.
- Post-coital bleeding: Sometimes, bleeding can occur after sexual intercourse in early pregnancy. This bleeding is usually from the cervix and does not harm the pregnancy.
- Constipation: In some cases, pressure by the hard stool on the congested cervix through the vaginal wall can cause bleeding.
Please note that bleeding accompanied by cramping, dizziness, or clotting requires immediate medical attention.
Key Tips:
- Monitor the severity and frequency of bleeding, noting any changes in color or flow. Use sanitary pads to monitor the amount and color of bleeding .
- Avoid strenuous activities to minimize risks.
- Consult your doctor immediately if bleeding is heavy, you pass clots or is you have cramps.
When is bleeding in early pregnancy serious?
Bleeding in early pregnancy can be due to some serious and harmful causes?
- Miscarriage: Often preceded by bleeding and cramping. If you have cramps or if your bleeding is heavy or becomes heavier over time, please consult your doctor immediately for an ultrasound.
- Subchorionic Hematoma: This is a type of bleeding that occurs between the uterine lining and the gestational sac. It is often accompanied by bleeding which may be mild . There may be no cramps. But the risks of sub-chorionic hematoma leading to a miscarriage is quite high.
- Ectopic pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition. In this condition, the fertilized egg implants and develops outside the uterus – usually in one of the Fallopian tubes. There is a high risk of rupture of the tubes. Tubal rupture can be a life-threatening condition. That is why, every case of bleeding in early pregnancy needs to be evaluated with an ultrasound to determine the source of bleeding.
Key Tips:
- Seek immediate medical care if heavy bleeding is accompanied by pain or dizziness.
- Be proactive by scheduling an ultrasound to confirm pregnancy health.
- Rest and avoid any activity that could increase abdominal pressure.
Managing First Trimester Bleeding
In the case of my patient, I found that she had a mild reddish bleeding per vagina. She did not have any abdominal cramps.
Speculum examination of the cervix showed a bluish congested cervix.
On ultrasound, I found that the pregnancy was healthy and situated inside the uterus. There was no sub-chorionic hemorrhage. The adnexa ( tissues around the uterus) were normal.
I reassured my patient that the bleeding was cervical in origin and unrelated to the uterus or pregnancy. I recommended the following steps to manage and prevent further complications:
- Rest as much as possible: Avoid physical exertion that increases cervical pressure.
- Avoid constipation: Consuming high-fiber foods and staying hydrated prevents strain on the cervix caused by hard stools.
- Abstain from sexual intercourse: This reduces cervical irritation and the likelihood of bleeding.
Conclusion
First trimester bleeding can be distressing but is not always indicative of a serious problem. Spotting and even some light bleeding are often normal. Identifying the cause through medical examination and ultrasound imaging can help reassure patients. Lifestyle adjustments, such as rest and dietary changes can help prevent bleeding.
If you have any pregnancy-related concerns or if you are experiencing early pregnancy discharge, consult a gynecologist online today to ensure your peace of mind and well-being.